Your Corpus Cavernosum
It is What Gives You An Erection!
Ever wonder what makes your erection hard?
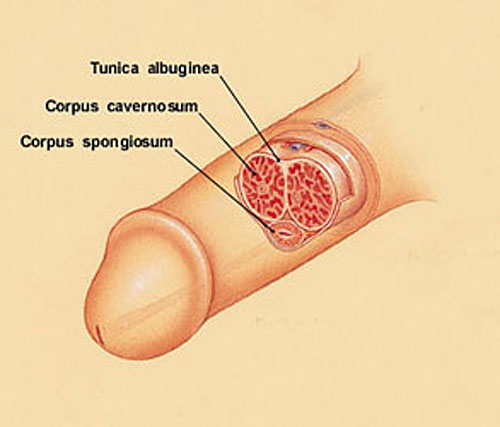
It is the corpus cavernosum (2 balloon like chambers in your penile shaft) filling up with blood until the sack that covers them (the tunica albuginea) is stretched tight. It's just like blowing a balloon up all the way.
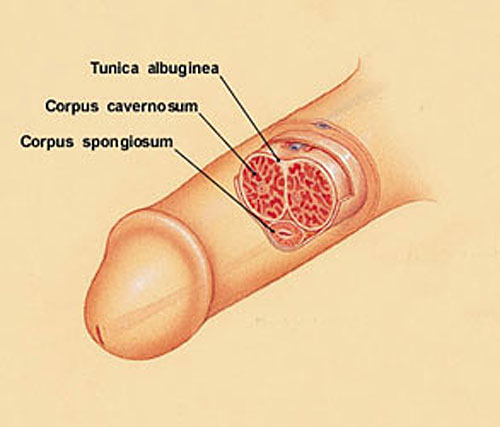
The corpus cavernosum are two sponglike tissues made up of smooth muscle and blood vessels. They begin at the pelvic bone and extend to just below the head of the penile shaft.
Now, a limp shaft is very much like an empty balloon. They both just kind of flop around. When the balloon is half full of air it feels soft and spongy. So does your penis when the corpus cavernosum are half full of blood.
When the balloon is fully blown up (and can stretch no further) it feels hard and tight. The same thing happens inside the shaft when these tissues are filled with blood and the tunica albuginea is stretched to it's limit.
How
Your Corpus Cavernosum
gives your an erection
Well the first thing that happens is you get sexually stimulated either mentally or physically.
Then your brain sends a message through your nerves to the bundles of nerves on either side of your prostate gland. (Your brain uses nitric oxide to transmit the message.) These nerves on the sides of your prostate gland are called "neurovascular nerve bundles".
All "neurovascular" means is that these nerves contol the blood flow into and out of your corpus cavernosum.
When the nitric oxide reaches the neurovascular nerve bundles an enzyme called Guanylate Cyclase is released. (An enzyme is a chemical that makes something happen.)
This enzyme turns another chemical called guanosine triphosphate (GTP) into Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).
Here's where all this starts to make sense: cGMP causes the smooth muscles lining the arterial walls to relax. This lets them expand.
At the same time the veins constrict (close up) so that blood does not leave easily.
This is what enables these chambers to fill up with blood.
Now, your shaft will continue to get bigger until the balloon like covering of these chambers (and the tunica albuginea chamber) is stretched to it's limit. And there you have a hard erection!
why your erection goes away
after sex
Now there is a second enzyme that works here. It is called Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE 5).
PDE 5 is usually released by your body just after you orgasm. It will also be released if you are no longer sexually excited.
PDE 5 is just the opposite of cGMP. PED 5 stops the relaxation of the arteries and relaxes the veins so the blood now flows through and out of your penis. Your erection gets small and softens.
That's the complete cycle of getting and losing an erection.
the horrible possible side effects
of
erectile dysfunction drugs
All the drugs you see advertised to help men who have trouble getting or maintaining an erection are PED 5 inhibitors.
These drugs prevent your body's PED 5 from breaking down the cGMP (which causes your erection) so your shaft stays filled with blood.
But, for these drugs to work you do need to be able to get sexually aroused. Without the presence of nitric oxide (sent from the brain during sexual arousal), the filling of the corpus cavernosum never begins.
Examples of oral PDE 5 inhibitors are sildenafil ( Viagra), varendafil (Levitra), and tadalafil (Cialis). All these drugs carry serious health risks.
In a healthy body,
no drugs are necessary
to maintain or sustain an erection.
Erectile enhancement drugs all increase blood pressure. All drugs that increase your blood pressure also come with the possible serious side effects of heart attack, stroke, blindness and death.
So, if you are contemplating using any of these erectile dysfunction drugs (or currently are using them), you may want to look into improving your overall health. Then you won't have any need for them.
A bent penis
is
easy to fix

If you have recently developed a bent penis, the bend is usually a problem with the corpus cavernosum itself.
A bent penis (Peyronies Disease) is usually the result of a scar (sometimes called a plaque) on the corpus cavernosum that is not allowing part of your corpus cavernosum, to expand normally.
Also, sometimes the bent penis is just a mild curve. This curved penis can also be caused by repeated stretching over and over again in a certain direction.
In either event, a bent penis is no real cause for concern and is very easy to fix.
A Hard Erection
And
A Healthy Body!
A normally healthy male body is capable of producing strong erections well into it's 90s!
Arteriosclerosis can inhibit the blood flow into these erectile chambers. So it is important to exercise, eat a proper diet, and eat the high Omega 3 (essential fatty acid, like from fish and fish oil) rich foods that keep your veins and arteries clean.
Nothing will cause arteriosclerosis faster than a diet high in sugars. Sugars NOT fats are responsible for clogging your arteries. Natural fats are healthy food!
All sugars interfere with the metabolism of proteins and fats. Refined sugars burn up the necessary vitamins necessary to burn fats. This is why fats accumulate in your veins and arteries.
Dehydration is another cause of arteriosclerosis.
Arteriosclerosis is reversible! So keep those veins and arteries as clean and clear as you possibly can. Exercise moderately and regularly, eat only healthy real foods, and drink plenty of clean fresh water.
When you are healthy, your corpus cavernosum will fill easily no matter how old you are. And you will be able to enjoy rock hard erections through your entire life!

Be Well.....
~ William










New! Comments
If you'd like to leave me a comment, please use the box below. Thanks! ~ William